About Radon
Everything you need to know about radon gas.
Where is radon found?
Radon can be found anywhere. Outdoor levels are usually very low, but indoor levels can be very high. It doesn’t matter where you live, how old your home is, or what type of foundation it has—the only way to know the level of radon gas in a home is to perform a test.
Are you at risk?

- An estimated 400 deaths per year in Iowa are caused by radon-induced lung cancer. That is approximately the same number of Iowans who die in traffic accidents each year. (United States Environmental Protection Agency, US EPA, and Iowa Department of Transportation)
- US EPA surveys in Iowa have found that 7 in 10 homes contain radon concentrations above the US EPA’s radon action level of 4 picoCuries/Liter (pCi/L).
- Iowa leads the nation in the percent of homes over the 4 pCi/L as well as percent of homes over 20 pCi/L.
- The average indoor radon concentration in Iowa is more than six times the national average.
How does radon get in your home?
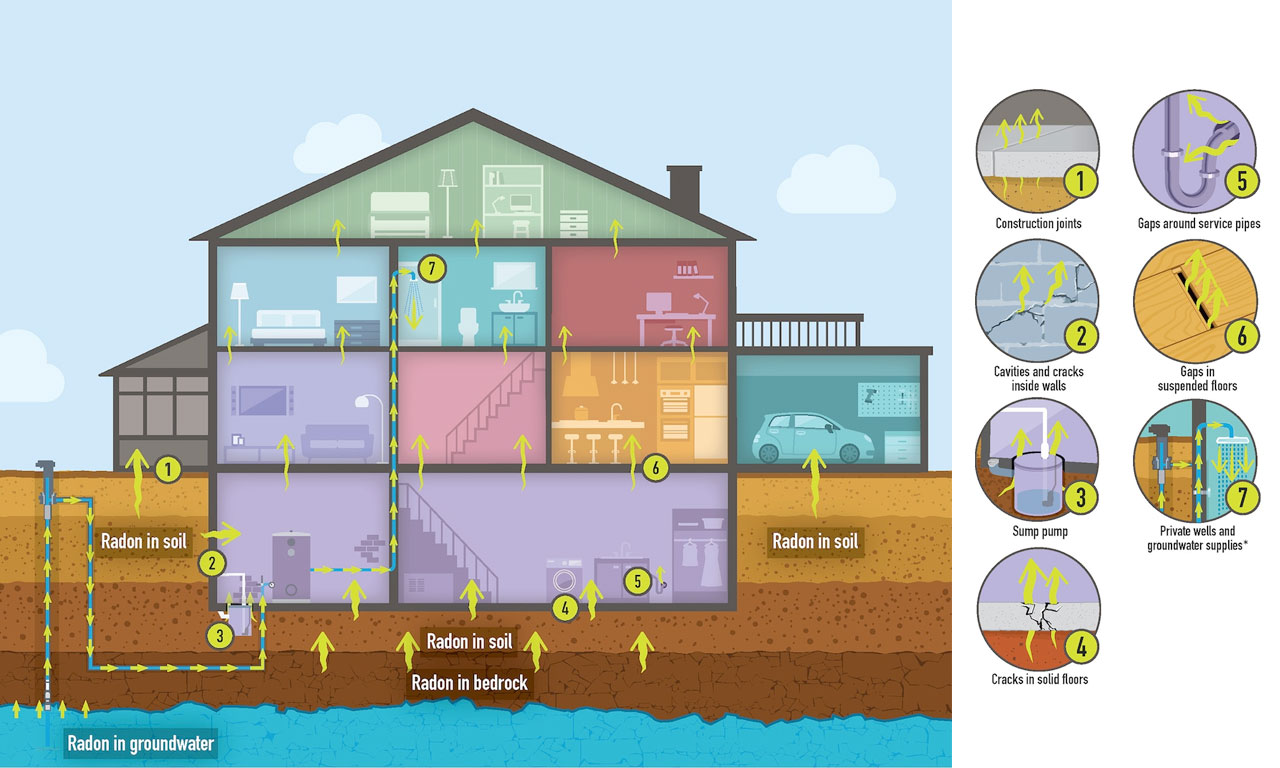
Radon gas rises up through the soil and is pulled into a house or building. It enters a home or building through cracks in the foundation, construction joints, gaps around service pipes or wires, and sump pits. It doesn’t matter what type of foundation your home has—basement, crawl space, slab—your home could have high levels of radon.
How do I test for radon?
Because radon can’t be detected by our senses, the only way to know if your home has high levels of radon is to test for it.
Everyone should test. Testing is easy and inexpensive to perform. It is suggested to test every 2 years or after renovating your home. The only way to know if your home has elevated radon concentrations is to test. Short-term tests can be done in 2-90 days, and long-term tests can be done in 90 days-1 year.
How do I take care of a radon problem?
Performing work to lower indoor radon levels is called radon mitigation. Radon mitigation is the process of installing a vent pipe and fan system within a home to reduce indoor radon levels. There are many ways to mitigate radon. The most common and effective is a vent pipe and fan system that draws air from underneath the foundation and vents it outside the home or building. This radon mitigation system removes radon from under the foundation and vents it above the roof line of the house so that it does not enter the home.

